Curiosity Sees Rare Clouds On Mars
Water ice or dry ice clouds on Mars?
Clouds on Mars are rare. With its thin atmosphere and scarcity of water, it’s not often there are the right conditions for clouds to form. The best time for clouds on Mars is during its coldest months near the Martian equator. Space scientists using the Mars Curiosity rover, which has been exploring the red planet since 2012, released these images of cloudy Martian skies on May 28, 2021.
The scientists said the clouds arrived a bit earlier and at higher altitudes than they expected. Clouds on Mars tend to form about 37 miles (60 km) above the surface and are made of water ice. But the clouds seen here are higher above Mars’ surface, where it’s so cold that they’re likely made of dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide) as opposed to water ice.
Scientists will need more studies to resolve with certainty which Martian clouds are water ice, and which are dry ice.
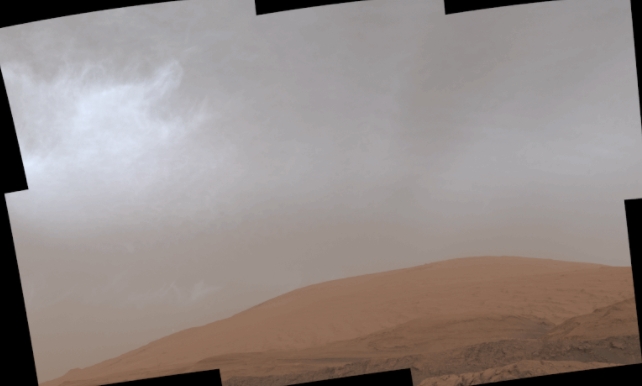
Cloudy sky in shades of gray over rusty dry rock outcropping.
The Curiosity rover took 21 individual images to create this image of how the Martian sky would appear to the human eye. Mont Mercou on Mars is in the foreground of this image taken March 19, 2021. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ MSSS.
Darker scene with rippled clouds moving out of frame.
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover took these images of noctilucent, or night-shining, clouds just after sunset on March 31, 2021. These clouds are composed of water ice, with the ice crystals reflecting the setting sun. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
Noctilucent clouds on Mars
Noctilucent, or night-shining, clouds appear after sunset when the sky has darkened on both Earth and Mars. After sunset on both worlds, particles high up in the atmosphere can still catch the sun’s rays and glow. Observers at high northern latitudes on Earth can catch sight of noctilucent clouds under the right conditions, typically beginning each year in late May or early June. They are beautiful to behold!
We can’t see the noctilucent clouds on Mars with our own eyes. But these sorts of clouds help space scientists determine how high up clouds are in the Martian atmosphere. Noctilucent clouds on Mars grow brighter as they fill with crystals, the scientists said, then darken as the sun sinks too low to continue to illuminate them.
A few white clouds on Mars drift off behind a dark hill.
More noctilucent clouds drifting over the landscape of Mars, imaged by Curiosity just after sunset on March 28, 2021. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
Iridescent clouds on Mars
Mars is a rocky, dusty and rather uniform planet as far as color goes. But it gets a splash of color with iridescent, or mother of pearl, clouds. Mark Lemmon of the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado, said:
If you see a cloud with a shimmery pastel set of colors in it, that’s because the cloud particles are all nearly identical in size. That’s usually happening just after the clouds have formed and have all grown at the same rate. I always marvel at the colors that show up: reds and greens and blues and purples.
It’s really cool to see something shining with lots of color on Mars.
Wispy white clouds with glowing pinks and blues.
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover took 5 images to create this shot of iridescent, or mother of pearl, clouds on March 5, 2021. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ MSSS.
Bottom line: Clouds on Mars are an infrequent phenomenon, and scientists are analyzing images taken by the Mars Curiosity rover to learn more about these elusive atmospheric delights.



 Creators of mankind
Creators of mankind Description of “Tall white aliens”
Description of “Tall white aliens” Where they came from?
Where they came from? About hostile civilizations
About hostile civilizations The war for the Earth
The war for the Earth “Tall white aliens” about eternal life
“Tall white aliens” about eternal life Video: “Nordic aliens”
Video: “Nordic aliens” Aliens
Aliens Alien encounters
Alien encounters The aliens base
The aliens base UFO
UFO Technology UFO
Technology UFO Underground civilization
Underground civilization Ancient alien artifacts
Ancient alien artifacts Military and UFO
Military and UFO Mysteries and hypotheses
Mysteries and hypotheses Scientific facts
Scientific facts